 Abbe
immediately took steps to diversify the product line of the firm. Carl
Zeiss had been against this diversification and had limited the company
to the production of microscopes and accessories. In his later years,
he was very conscious of limiting the risk associated with the business
to protect the inheritance of his children.
Abbe
immediately took steps to diversify the product line of the firm. Carl
Zeiss had been against this diversification and had limited the company
to the production of microscopes and accessories. In his later years,
he was very conscious of limiting the risk associated with the business
to protect the inheritance of his children.
Abbe used his knowledge of the new Schott glasses and passed the responsibility for the new products to technical staff that he had been developing for the past 5-10 years. His major scientific interest remained in the area of prism binoculars. He gave the responsibility for measuring devices to Carl Pulfrich, photographic lenses to Paul Rudolph, the day to day operation of the firm to Siegfried Czapski and continued to develop new scientists to head other newer departments.
He found Max Pauly who had experience with large telescope construction as a side business while working full time as a manager of a sugar production plant. Within a few years, they were constructing telescopes and accessories for general commercial use and, surprisingly, large scale observatory telescopes. These were manufactured and erected in the Zeissworks in Jena for quality control purposes and deconstructed and then moved to the customer's site to be final constructed.
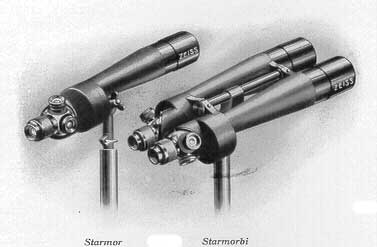 The
early part of the 20th Century saw tremendous innovation with regard to
the development of binoculars, telescopes and military optics. This particular
design became a commercial success after its military use in World War
I. It featured a 60 mm objective and three eyepieces magnifying 12x, 24x
and 42x. The telegraph ordering word was Starmor for the monocular and
bi added as a suffix for the binocular. This obviously need a tripod or
table pod and was sold with a choice of either.
The
early part of the 20th Century saw tremendous innovation with regard to
the development of binoculars, telescopes and military optics. This particular
design became a commercial success after its military use in World War
I. It featured a 60 mm objective and three eyepieces magnifying 12x, 24x
and 42x. The telegraph ordering word was Starmor for the monocular and
bi added as a suffix for the binocular. This obviously need a tripod or
table pod and was sold with a choice of either. This
illustration shows three different configurations of the same Zeiss telescope
available in 1934. The upper left illustration was used in various catalogs
dating back to 1914 and featured the famous Matterhorn in the background
. You can see that the instrument required a strong mounting system and
dwarfed the user.
This
illustration shows three different configurations of the same Zeiss telescope
available in 1934. The upper left illustration was used in various catalogs
dating back to 1914 and featured the famous Matterhorn in the background
. You can see that the instrument required a strong mounting system and
dwarfed the user.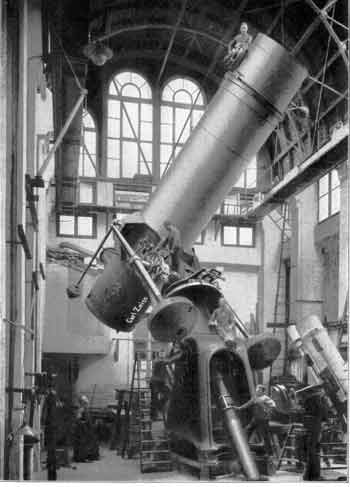 The
smaller telescopes available to the general public were possible because
of the research and development of larger scale projects that Zeiss was
contracted to accomplish for various museums, observatories and universities.
The
smaller telescopes available to the general public were possible because
of the research and development of larger scale projects that Zeiss was
contracted to accomplish for various museums, observatories and universities. In
the years before World War I, Zeiss was approached by the German National
Museum in Munich to propose a design for a planetarium. As a result, Zeiss
constructed two planetariums. One was a physical representation of the
planets around the sun. However, they were challenged to do something
unique. World War delayed a proposal but during the years immediately
after the war, Zeiss's head of R&D proposed a unique projector.
In
the years before World War I, Zeiss was approached by the German National
Museum in Munich to propose a design for a planetarium. As a result, Zeiss
constructed two planetariums. One was a physical representation of the
planets around the sun. However, they were challenged to do something
unique. World War delayed a proposal but during the years immediately
after the war, Zeiss's head of R&D proposed a unique projector.